We may earn money or products from the companies mentioned in this post.
3D Printer Selection Guide
The capability of 3D printing offers a world of creativity and innovation, opening doors to personalized objects, intricate models, and even functional prototypes that were once the domain of large manufacturers. As an adult entering this exciting arena, understanding the array of 3D printer options can seem daunting. Whether you’re a hobbyist looking to bring your ideas to life, an educator aiming to inspire the next generation, or a professional seeking to prototype designs, this essay will serve as your compass. By demystifying the core technologies behind 3D printing, comparing critical performance factors such as print quality and speed, and evaluating practical considerations like build volume and material compatibility, you’ll become equipped to choose a 3D printer that not only suits your immediate needs but also supports your creative journey ahead. Furthermore, insights into the user experience and the value of community support will ensure you’re not just buying a machine, but stepping into an ecosystem that will foster your growth in the world of 3D printing in this 3D printer selection guide.
Understanding 3D Printing Technologies
3D Printing Innovations: Exploring the Key Technologies Reshaping Manufacturing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is defined by a variety of technologies that cater to different needs within the industry. Among these technologies, three stand out for their prevalent use and unique capabilities. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) are the pillars holding up the vast landscape of 3D printing applications.
FDM works by extruding thermoplastic filaments through a heated nozzle, layer by layer, until a physical object takes shape. It’s a versatile technology favored for its ease of use, speed, and cost-effectiveness. This method is perfect for hobbyists and professionals alike, crafting everything from prototype parts to functional household items. It also provides an eco-friendly edge, as materials like PLA are biodegradable, aligning with environmentally conscious practices.
On the sophisticated end, SLA harnesses the power of UV light to cure liquid resin into hardened plastic. It promises high-resolution results with intricate details, making it ideal for the dental industry, jewelry design, and any field demanding precision. SLA printers offer a smooth finish, often bypassing the need for post-processing, thus streamlining the manufacturing workflow. Meanwhile, SLS takes a different approach by fusing powder particles together using a high-powered laser. It unlocks a world of potential in creating durable and complex geometries that are often impossible with traditional subtractive methods. SLS’s ability to manufacture parts without support structures reduces material waste and offers freedom in design, which is highly valued for producing functional parts and prototypes across sectors such as automotive and aerospace.
Collectively, these technologies represent 3D printing’s transformative impact on manufacturing, providing tools that span the spectrum from entry-level to industrial-grade production. They continue to evolve, pushing the boundaries of innovation and offering solutions to increasingly complex challenges in the modern world of manufacturing and design. As these technologies advance, they not only democratize production capabilities but also inspire a new era of makers and creators equipped with the power to bring their most intricate visions to life.

Determining Print Quality and Speed
When deliberating printer choices, two pivotal factors play a decisive role: print quality and speed. These elements are particularly critical for businesses where print quality can affect the perceived professionalism of marketing materials or the clarity of detailed designs, while speed influences workflow efficiency and productivity.
Print quality is gauged by the resolution, measured in dots per inch (DPI). The higher the DPI, the finer the detail a printer can reproduce, thus ensuring crisp text and vivid images which are essential for high-stakes presentations or client-facing documents. Advanced printers tout resolutions surpassing 2400 DPI, but with elevated resolution comes a steeper price tag – a trade-off worth consideration for sectors like graphic design or architecture, where precision is paramount.
Conversely, print speed, indicated in pages per minute (PPM), dictates the operational pace of an organization. High-speed printers, essential for high-volume print tasks, enable businesses to handle large print jobs efficiently without bottlenecks. Nevertheless, it’s the equilibrium between speed and quality that defines the optimal printer choice. Laser printers, renowned for swift output, are favored in environments with voluminous text document needs. However, when superior detail is mandatory, inkjet printers, albeit slower, offer superior resolution. Ultimately, identifying the right balance tailored to specific requirements is crucial for an investment that aligns with organizational demands and enhances productivity.
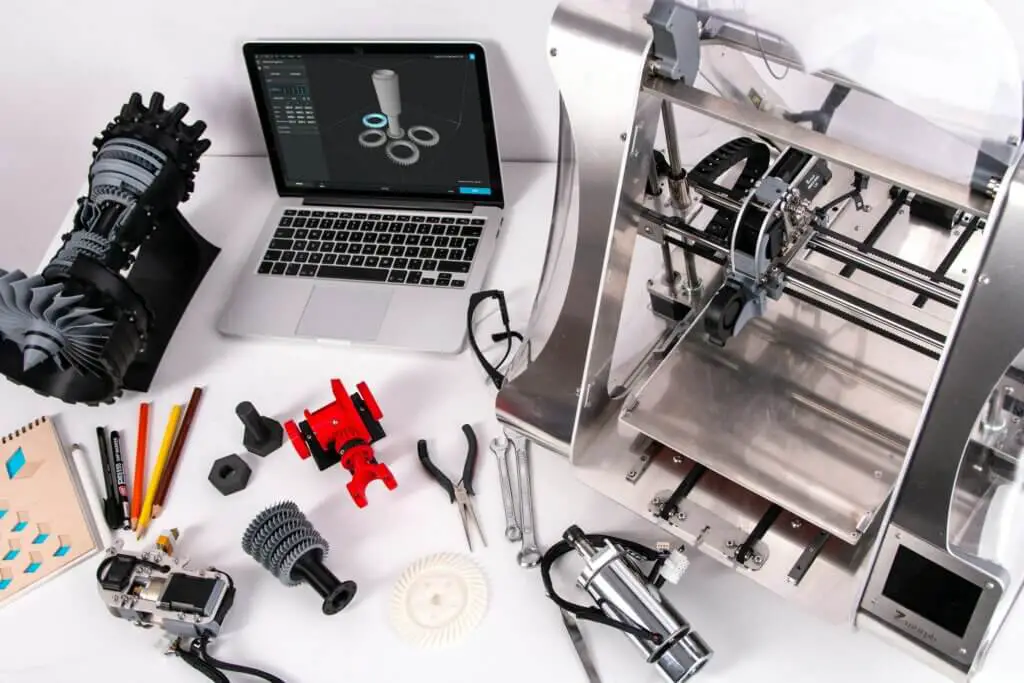

Assessing Printer Build Volume and Material Compatibility
When dealing with 3D printing, build volume and material compatibility emerge as pivotal aspects to consider before acquiring a 3D printer. Build volume, which denotes the maximum size that a printer can fabricate an object, is paramount as it directly influences the scope and scale of projects one can undertake. A printer with a generous build volume allows for the crafting of large, intricate designs without the need for assembling multiple smaller pieces post-printing. This capacity is critical for both commercial applications, where large, robust parts may be necessary, and individual enthusiasts who aim to push the boundaries of creative expression.
Material compatibility, on the other hand, stands as a testament to the versatility of a 3D printer. The burgeoning market of 3D printing materials, from basic plastics such as ABS and PLA to advanced composites and even metals, demands that printers can adapt to a wide array of substances. This adaptability ensures that users can select the optimal material for the specific properties required by their project, be it flexibility, strength, thermal resistance, or aesthetic quality. Choosing a printer capable of handling diverse materials not only future-proofs the investment but also opens a plethora of possibilities for innovation, whether in prototyping, custom manufacturing, or artistic endeavors. A keen understanding of the interplay between build volume and material compatibility ultimately empowers users to make informed decisions that align with their project needs and ambitions in the ever-evolving landscape of 3D printing.

Considering User Experience and Community Support
If you are assessing 3D printers for potential acquisition, considering the user experience is crucial. An intuitive user interface ensures a smooth learning curve, thereby preventing common operational errors. Printers offering straightforward software with clear instructions enhance the overall efficiency. In addition, machines that provide real-time feedback and adjustments contribute to a better user experience by enabling users to fine-tune prints on the fly, thus ensuring desired outcomes more reliably.
Strong printer model community support plays another significant role in the selection process. A vibrant community signals a wealth of shared knowledge and resources, which can be invaluable for troubleshooting and enhancing printer performance. Active forums where users exchange mods, tips, and optimized print settings are assets that amplify a printer’s value. Moreover, community-created content such as detailed how-to guides and video tutorials can drastically reduce downtime, making community support an indispensable component for both novices and seasoned users alike. In essence, a 3D printer backed by a supportive community can simplify problem-solving, expand the printer’s capabilities, and foster a collective advancement in 3D printing practices.
Some Popular 3D Printers
Several 3D printers have garnered popularity in recent years, offering cutting-edge capabilities and versatility for both enthusiasts and professionals. The Prusa i3 MK3S, renowned for its reliability and affordability, stands as a top choice with its user-friendly interface and excellent print quality. Creality’s Ender 3 series has also made waves in the market, boasting a large community following and impressive performance-to-price ratio. For those seeking high-end industrial-grade printing, the Formlabs Form 3 provides exceptional precision and detail, utilizing advanced SLA technology. Meanwhile, the Ultimaker S5 appeals to professionals with its large build volume and reliability for complex projects. These printers showcase the diverse range of options available, catering to various needs and budgets within the rapidly expanding 3D printing community. All could be excellent choices depending on your personal 3D printing needs.

Armed with knowledge of different printing technologies, factors affecting print quality and speed, and considerations for build volume and materials, you’re now better positioned to make an informed selection. More than just a tool, the 3D printer you choose will be your companion in exploration and creativity, bolstered by the user-friendly interfaces and the supportive community that surrounds it. As you stand at the threshold of possibility, remember that your 3D printing adventure is a continuous learning experience, one that is limited only by the bounds of your imagination and the capabilities of the printer you select. Embrace the potential, and let your creative vision take shape in the tangible world.
You Might Also Like – How Much is a 3D Printed Home?

